¶ What is a DPIA?
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a process that helps organizations identify, assess, and manage risks related to the processing of personal data. The purpose is to ensure that the processing is necessary and proportionate to its objectives while protecting individuals' rights and freedoms.
¶ Why conduct a DPIA?
A DPIA is required when a type of processing is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals. This is particularly relevant when using new technology or when the nature, scope, purpose, and context of the processing suggest a significant impact. A DPIA helps ensure compliance with data protection regulations and demonstrates that the organization has taken the necessary measures to meet legal requirements.
¶ How to conduct a DPIA
To conduct a DPIA, organizations should follow these steps:
- Describe the processing – Provide a systematic description of the planned processing activities and their purpose.
- Assess necessity and proportionality – Evaluate whether the processing is necessary and reasonable in relation to its objectives.
- Conduct a risk assessment – Analyze the risks that the processing may pose to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
- Implement risk mitigation measures – Identify and plan actions to manage and reduce risks while ensuring compliance with the GDPR.
It is essential to document the entire process and involve relevant stakeholders, including Data Protection Officers (DPOs) and senior management, to ensure a thorough and effective assessment.
For detailed guidance and checklists, visit the Norwegian Data Protection Authority’s website: datatilsynet.no.
¶ How to conduct a DPIA in Diri
You can either start a DPIA through the feedback step in the pre-DPIA process (from the processing activity) or via ‘DPIA’ in the left menu.
The DPIA process consists of four steps. During each step, the different parts of the impact assessment are documented. You can see the overall process, with the four steps, in the image below.
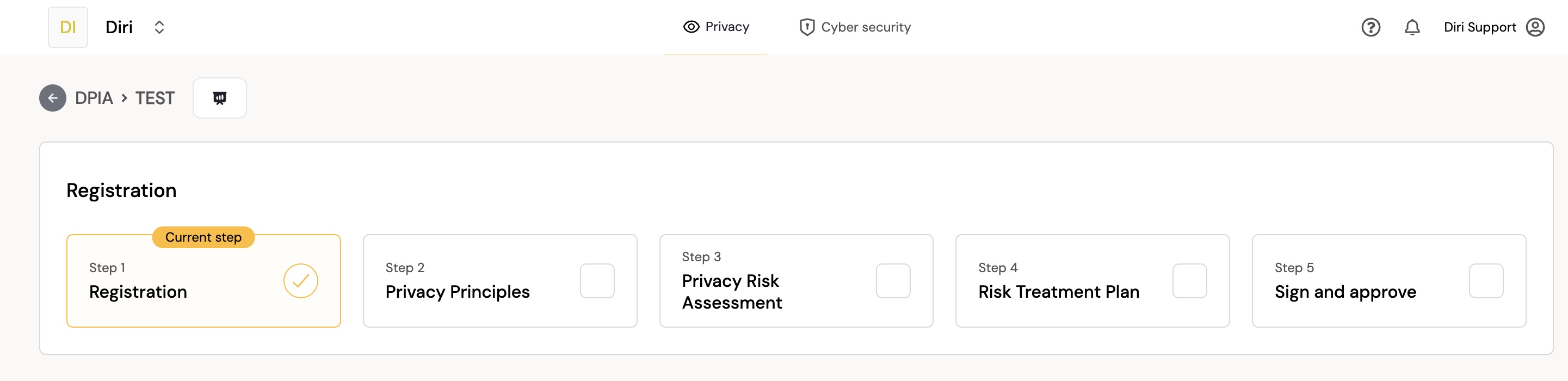
¶ Step 1 Registration
In step 1, information about the current impact assessment is recorded. This includes the name of the DPIA, who is responsible for it, what is to be assessed (e.g., an IT system or another processing activity), who will participate, and any scope limitations.
¶ Step 2 Privacy Principles
This step provides comprehensive guidance for conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). It is designed to help organizations navigate the complexities of data processing while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and safeguarding individuals’ rights. The following sections will detail the purpose of data processing, methods for data collection, identification of data sources, and principles of data minimization. Additionally, it will cover the selection of legal bases for processing, the impact on data subjects, data retention policies, and the implementation of data security measures. By adhering to this guidance, organizations can effectively manage privacy risks and maintain high standards of data protection.
¶ Guidance for DPIA in Diri step 2
Purpose of Data Processing
- Define why the data processing is carried out.
- Assess whether it is necessary or if less intrusive alternatives exist.
Data Collection
- Specify what types of personal data are collected and processed.
- Select data collection methods (e.g., forms, interviews, sensors).
- Indicate whether sensitive personal data is processed.
Data Sources
- Identify the origin of the data (directly from individuals, third parties, public records, etc.).
Data Minimization
- Assess whether the amount of data collected is proportionate to the purpose.
Legal Basis
- Select the appropriate legal basis for processing (consent, contract, legal obligation, etc.).
Data Subjects and Impact
- Define which groups the data concerns (children, patients, elderly, etc.).
- Describe how individuals will be informed and how they can exercise their rights.
Data Retention
- Specify how long the data will be retained and any deletion processes.
Data Security and Sharing
- Describe security measures for storage (e.g. encryption, access control).
- Indicate measures to protect data when shared (e.g. data processing agreements, confidentiality).
- Specify if data will be transferred outside the EEA and how compliance will be ensured.
Privacy Impacts
- Identify potential negative impacts on individuals' privacy and rights.
¶ Step 3 Privacy Risk Assessment
In this step, you conduct the risk assessment. Note that it is privacy risks that should be assessed.
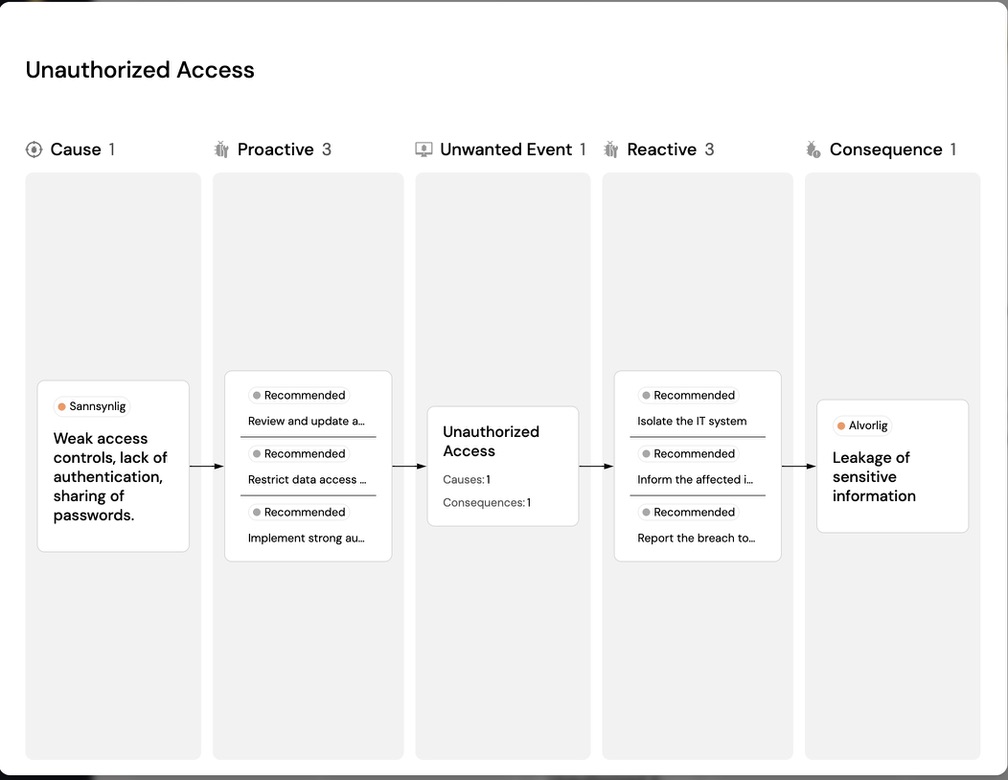
Start by identifying undesirable events, the causes of these events, and the consequences that may follow.
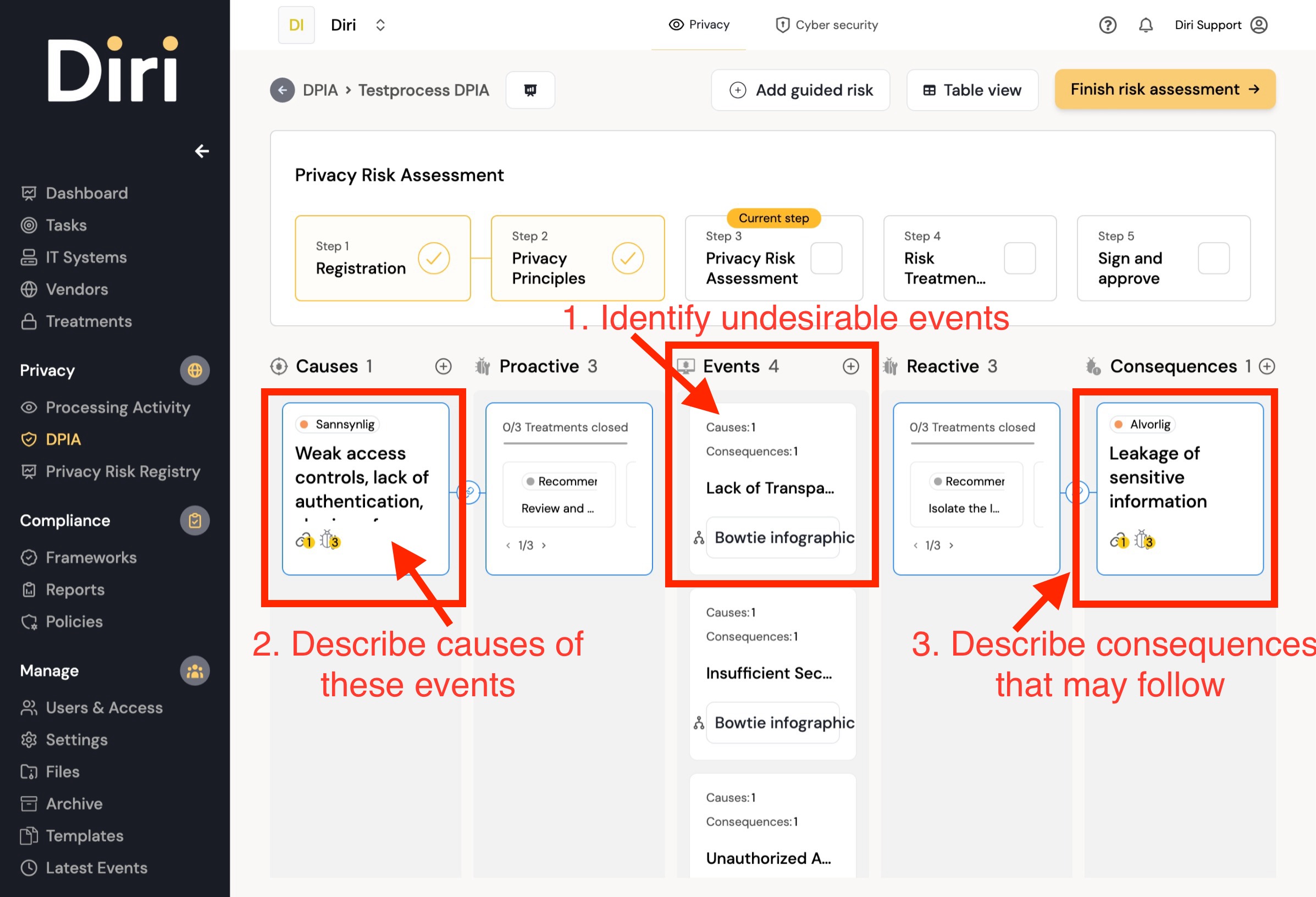
Then propose risk-reducing measures, both preventive (Proactive) and impact-reducing (Reactive).

Then click on ‘Bowtie infographic’ to see how everything is connected.
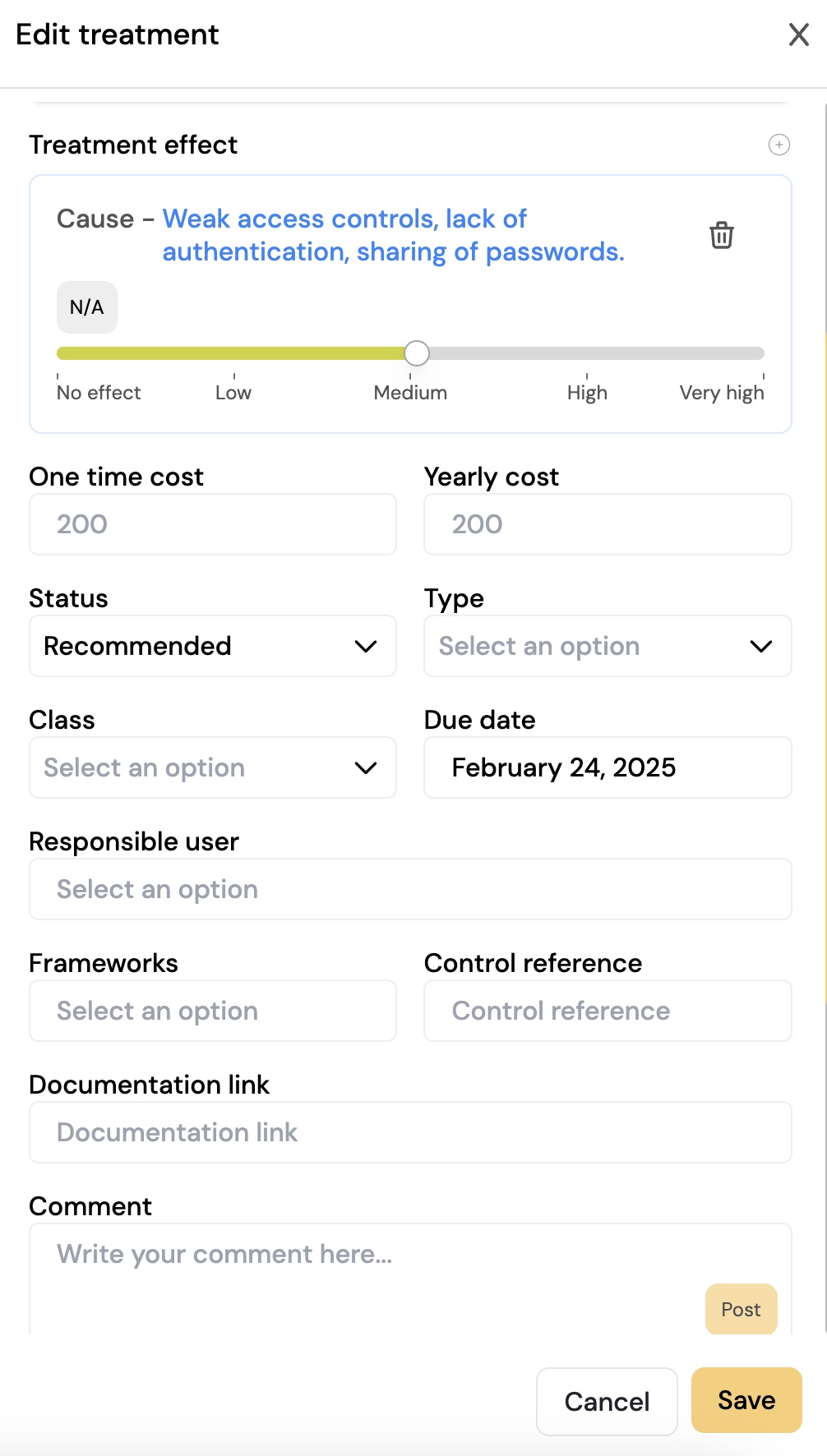
The treatments you have documented in the risk assessment will be included in a treatment plan.

For each measure, you can describe who is responsible, the cost of implementation, the deadline for completion, etc.
Now you are at the end of the process where the action plan must be approved and signed by the person responsible in the organization.
